Edifice:Python 声明式 UI 库
介绍
最近喜欢用 Python 写 PyQt 程序。但是有一点不太爽,PyQt 采用传统命令式编程,开发起来太费劲。了解前端的小伙伴都知道,现在流行声明式编程,开发效率和体验都大幅提升,用过就回不去了。
Python 的生态丰富度,在所有编程语言中是位列第一梯队的。只要有一个想法,定能找到好几个开源库。这不,搜索 Python 响应式 UI 库,就找到了本文的主角 Edifice。
Edifice 是一个 Python 下构建响应式界面的 UI 库。来自前端生态的启发(比如 React)。特色功能:
- 来自前端实践的现代化范式,更加容易地创建 UI
- 支持 Hot Reload 热重载
- 与 Python 生态无缝衔接
- 原生桌面程序,没有浏览器套壳那么重
Edifice 使用 Qt(PySide/PyQt5)作为后端。
Getting Started
安装包:pip install pyedifice
Hello World:
import edifice
from edifice import Label
edifice.App(Label("Hello World!")).start()
热更新
开启方式:
python -m edifice tutorial.py MyApp
Component Inspector
Edifice 还带有一个组件检查器,能够辅助调试组件树以及状态变化。开方式:
python -m edifice --inspect tutorial.py MyApp
官方 Examples
| 项目 | 备注 | 截图 |
|---|---|---|
| Calculator | 100 lines of code |  |
| Financial Charting | 响应式,自动更新
200 lines of code 结合绘图功能 |
 |
| Forms | 基于 Form 组件高效开发表单 |  |
| Harmonic Oscillator | 响应式图表
自定义动画 30fps 运行 |
 |
Qt Backend
Edifice 对 PySide2 和 PyQt5 都支持。Edifice 默认使用 PySide2。
如果希望使用 PyQt5,分为两步。
首先,通过以下方式安装 pyedifice 包,可以不装 PySide2:
# A dependency required for dynamic reloads
pip install watchdog
# A dependency required for asyncio integration
pip install qasync
pip install --no-dependencies pyedifice
然后通过一个环境变量选择使用那种后端:
export EDIFICE_QT_VERSION=PyQt5
组件
Edifice 应用由 Component 和 App 组成。
Component 是构成应用的基本单元,状态 + UI。Edifice 是一个组件化框架,整个应用由组件构成。
组件分为两类:
- native components:Qt View、Button、Text
- composite components:对 Component 组合后的组件
在 Edifice 中,组件的声明方式如下:
import edifice as ed
from edifice import Label, TextInput, View
# Declare your own component, MyApp.
# The render function describes how your custom component is to be rendered
class MyApp(ed.Component):
def render(self):
return View(layout="row")(
Label("Measurement in meters:"),
TextInput(""),
Label("Measurement in feet:"),
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
ed.App(MyApp()).start()
组件的状态分为两类,一类是内部状态 State,一类是外部属性 Props。
Props
Props 是由外界传入的属性,声明方式:
class Foo(Component):
# don't worry about this for now
@edifice.register_props
def __init__(self, a, b, c):
# a, b, c are the props
pass
# Create a Foo with props a=1, b=2, c=3.
Foo(a=1, b=2, c=3)
其中:
- @edifice.register_props 是一个注解,用于自动保存 props
- props 被存入 self.props 字典
- 组件内获取 props 两种方式:self.props["value"] 或者 self.props.value
- 在组件内,props 是只读的,不可更改
State
State 表示组件的内部状态。
状态在构造函数中初始化。跟通常的创建类成员无异。
组件内部可以通过 set_state 方法刷新状态。之后会触发 render 方法 UI 刷新。
注:通过覆写 should_update 方法,可以控制是否拦截 UI 刷新。
状态更新示例:
self.timer = edifice.Timer(
lambda: self.set_state(seconds=self.seconds+1))
render
render 是组件的核心方法,用于根据状态生成对应的 UI。示例:
def render(self):
return View(layout="column")(
View(layout="row")(
Label("Username: "),
TextInput()
),
View(layout="row")(
Label("Email: "),
TextInput()
),
)
Stateful Component
有状态组件,能够维护初始状态,保存状态属性。组件内部可以使用 set_state 方法更新状态。组件会通过 render 方法重新绘制:
import edifice
class Timer(edifice.Component):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.seconds = 0
self.timer = edifice.Timer(lambda: self.set_state(seconds=self.seconds+1))
def did_mount(self):
self.timer.start(1000)
def render(self):
return edifice.Label(self.seconds, style={"width": 80, "height": 30, "font-size": 20})
edifice.App(Timer()).start()
Stateless Componet
Edifice 也是支持无状态组件的,或称为 React 中的函数式组件。
通过 make_component 注解,能够将一个函数转换为组件,适合于没有内部状态的组件。
状态管理器
状态管理是应用开发的难点,状态管理器是目前前端领域常用的最佳实践。Edifice 也提供了一个状态管理器。
Edifice 中组件像 React 一样,将状态从上向下传递。这里有一个问题,如果父组件状态变化,所有子组件都要更新,导致性能浪费
Edifice 提供了 StateValue 和 StateManager 进行状态管理。
StateValue
StateValue 是 Edifice 可跟踪的状态,用于响应式订阅,核心方法是 set 和 subscribe。
subscribe 只能在 render 中调用,或者在 mount 之后调用。
如果状态改变,将会重绘。使用方法:
def render(self)::
# Assume USER is a module-level variable
user = USER.subscribe(self)
# Assume balance is passed from a parent
balance = self.props.balance.subscribe(self)
return Label(f"{user}: {balance}")
其中:
- 包含两个用例:USER 是模块级别的,balance 从父组件传入的
状态更新:
def on_click(self):
USER.set(self.text_input_value)
StateManager
StateManager 的概念跟 StateValue 类似,可以将它理解为管理多状态的 Key-Value 存储。
StateManagers 允许将相关联的状态存储到一起,并且进行批量更新。
组件订阅的是 StateManagers 中单独的 key,与 key 绑定的还是 StateValue。
方法:
- subscribe:将组件与某个 Key 相绑定
- set:更新 key 值
- keys:获取所有的 Key
Window
在窗口中展示子组件。
| 示例 | 效果 |
|---|---|
class MyApp(Component):
def render(self):
return View()(
Window(title="Hello")(
Label("Hello")
)
)
App(MyApp()).start()
|
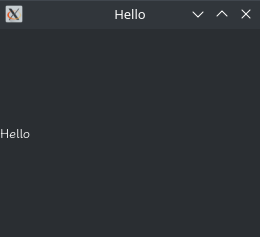 |
注:官方文档的 Demo 有误。
窗口和视图的区别?窗口支持一系列参数:
- title:窗口标题
- icon:窗口图标
- menu:菜单栏
- on_close:窗口关闭时的回调函数
View
基础布局组件。越界的内容将会被截断。如果需要滚动,使用 ScrollView。
属性:layout(str):
- 取值 row、column、none
- none 表示绝对布局,子组件可以通过 left、top 调整绝对位置
TabView
Tab 分页组件。
| 示例 | 效果 |
|---|---|
class MyApp(Component):
def render(self):
return View()(
TabView(labels=['Label1', 'Label2'])(
View()(Label('I am tab1')),
View()(Label('I am tab2'))
)
)
App(MyApp()).start()
|
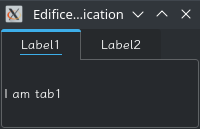 |
属性 labels:标签分页属性。
CustomWidget
edifice 自带的视图控件很少,但是提供了 CustomWidget 组件,供开发者自己封装。示例:
class MyWidgetComponent(CustomWidget):
def create_widget(self):
# This function should return the new widget
# (with parent set to None; Edifice will handle parenting)
return QtWidgets.FooWidget()
def paint(self, widget, newprops):
# This function should update the widget
for prop in newprops:
if prop == "text":
widget.setText(newprops[prop])
elif prop == "value":
widget.setValue(newprops[prop])
覆写了两个方法:
- create_widget:创建一个 Qt Widget
- paint:解析 newprops,对 widget 进行一顿设置
布局
Row 横向布局
import edifice as ed
from edifice import Label, TextInput, View
window = View(layout="row")( # Layout children in a row
Label("Measurement in meters:"),
TextInput(""),
Label("Measurement in feet:"),
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
ed.App(window).start()
UI 控件
IconButton
图标按钮。Edifice 捆绑了 FontAwesome,能够直接使用图标库里面图标,图标列表。
属性:
- name:FontAwesome 图标名称
- size: int 大小
- collection:图标集,当前只支持 FontAwesome
- sub_collection:图标子集,如 regular 或者 solid
- color:颜色,一个 tuple (R, G, B, A)
- rotation:旋转角度
TextInput 输入框
监听输入内容变化:
TextInput(meters, style=input_style,
on_change=lambda text: self.set_state(meters=text)),
props:
- text:输入内容
- on_change:Callable[[str], None] 内容变更回调
- on_edit_finish:Callable[[], None]
- completer:文本补全